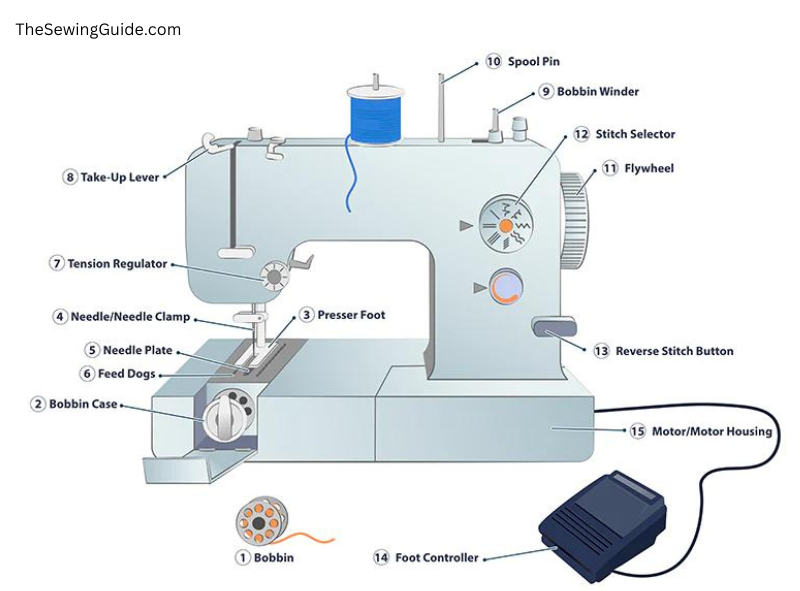
Sewing machines are complicated and intricate equipment made up of numerous interrelated components and mechanisms, each having a specialised function that adds to the machine’s overall performance. To completely comprehend how a sewing machine works, it is necessary to investigate its anatomy. Each component, from the needle and feed dogs to the spool pin and presser foot, plays an important function in the sewing process, ensuring that stitches are exact, even, and long-lasting. In this article, we’ll explore and analyze the anatomy of sewing machines.
🧵✨ Sew-per Fun-damentals: The Magical Anatomy of a Sewing Machine! ✨🧵
The term “basic components of a sewing machine” describes the fundamental pieces or parts required for a standard sewing machine to function. Each of these fundamental parts has a particular purpose that helps the machine as a whole work, enabling it to produce a range of stitches and produce various stitching outcomes. They comprise:
- Spool Pin: A little metal rod known as a spool pin is located on the sewing machine’s body. Spool pins serve primarily to grab thread spools. Spool pins are typically 2 to 4 inches long, about the width of a chalk, and made of plastic or metal. To unreel the thread, it enables the spool to revolve as desired.
- Thread Guide: A thin metal or plastic component that aids in threading from the spool to the needle.
- Needle: A thin metal instrument with a sharp edge that pierces cloth to form a stitch. Straight and curved needles are the two primary kinds of needles. Straight needles are the most popular and are found in a broad variety of sewing machines. Curved needles are usually used in blind stitching machines.
- Needle Clamp: It is a structure that safeguards the needle in place.
- Handwheel: The handwheel is a hand control on a sewing machine that lets you to move the needle upside and downside. As the handwheel is spun, the machine’s internal mechanism turns, making the needle to move up and down.
- Bobbin: A bobbin is the little spool of thread that stays at the bottom of your sewing machine. The machine stitches by combining the bottom thread of the bobbin by taking the top thread which runs through the needle.
- Bobbin Case: A little metal or plastic component that maintains the bobbin in position and adjusts the tension of the bottom thread.
- Presser Foot: A presser foot maintains the cloth firm when sewing, suppressing it from slipping and sliding with the needle.
These parts work together to produce a wide range of stitches, from simple straight stitches to complicated artistic patterns, causing the sewing machine a fantastic equipment for anybody fascinated in stitching.
Sew-mazingly Complex: Get to Know the Brainy Bits and Bobs of Your Sewing Machine!
Sewing machines are made up of several intricate parts that work together to produce a wide range of stitches and designs. Some of the most significant and sophisticated parts of a sewing machine, as well as their functions, are as follows:
- Feed dogs: It is made of metal teeth that move while you sew, softly grasping the bottom cloth to assist it flow through the sewing machine and produce an excellent stitch.
- Tension dial: Tension dial manages the tension of the top thread, which is necessary for consistent sewing and preventing thread damage. The tension dial regulates the pressure given to the tension disk, which grab the top thread as it runs through the machine.
- Stitch selection mechanism: The stitch selection mechanism provides a way to pick between several stitch types such as straight stitch, zigzag stitch, and fancy stitching. In manual machines, this is almost always a knob, but on automated systems, it is usually a button.
- Automatic thread cutter: The automated thread cutter is a sophisticated component that allows the you to autonomously clip the thread at the end of a seam. It employs a motor-driven blade that is timed to cut the thread at the appropriate point.
- Stitch regulator: A stitch regulator is a sophisticated device that aids in the maintenance of an uniform stitch length when sewing at fast rates or on uneven textiles. It works by regulating the machine’s motor speed to match the pace of the cloth as it passes through the machine, assuring that each stitch has a uniform length.
- Reverse lever: The reverse lever is a tool that enables you to sew back the other way, strengthening threads at the start and end of a seam. It operates by abruptly reversing the motor’s direction, making the needle to go backwards instead of forwards.
These specialised components are crucial because they allow the sewing machine to execute a range of activities and functions that would be challenging or not possible with simpler systems. These components make the sewing machine operate at a higher level.
Clean Machine, Happy Seamstress: Tips and Tricks to Keep Your Sewing Machine Running Smoothly!
A sewing machine must be properly cleaned and maintained in order to function properly and avoid malfunctions. The following advice will help you maintain and clean your sewing machine:
- Replace needles frequently: It’s simple to overlook the amount of labour your needle does. The dulling of needles over time can cause missed stitches, looped threads, cloth pulls, and even machine damage. After 8 hours of usage or at the first indication of wear or damage, replace the needle.
- Oil the machine: Sewing machines, like the majority of other devices, benefit from routine lubrication. There are several internal mechanical devices in sewing machines. The machine will operate more gently and efficiently if it is oiled.
- Yearly servicing: Make it a point to get your equipment professionally serviced once a year to maintain it running at peak efficiency. When you regularly get your equipment repaired by a professional, its lifespan will be significantly increased.
- Use a lint roller: Lint and dust may be quickly and simply removed from the outside and interior of your machine with a lint roller.
- Regularly clean the machine: To clean out any dust particles, fur, or waste from the machine’s exterior, use a lint roller or brush. To clean the interior of the machine of dust and lint, use a gentle brush or vacuum connector. To prevent the equipment from being damaged, make sure you sweep away all debris.
Read More: Best Singer Sewing Machines: A Veteran’s Top Picks
Conclusion
Ultimately, a sewing machine is made of simple pieces like the handwheel, spool pin, and bobbin winder, as well as more sophisticated parts like the feed dogs, tension dial, needle bar, and hook assembly. These intricate elements serve critical functions in ensuring that the machine stitches correctly and consistently. To keep your sewing machine functioning smoothly, clean and maintain it on a regular basis, which includes cleaning dust and lint from the exterior and inside, oiling the machine, and inspecting the thread route for tangles or knots. By properly maintaining your sewing machine, you can ensure that it will continue to work effectively and create high-quality stitches for many years to come.

I love sewing, I am sewing for the last 15 years and started this blog with the help of my niece to spread sewing-related guides all over the world.
Sewing could be a full-time profession or hobby, and I wish to make a change by adding more people to the sewing world.